The art and culture of ancient Egypt stand as an enduring testament to the sophistication, creativity, and spiritual depth of one of the world’s oldest civilizations. Spanning over three millennia, from around 3100 BCE to 30 BCE, ancient Egyptian art and architecture not only reflected the beliefs and values of the society but also left an indelible mark on the course of art history. In this exploration, we delve into the captivating world of the arts of ancient Egypt, examining the rich tapestry of visual expression that has fascinated and inspired generations.
1. The Artistic Flourish of Ancient Egypt: A Historical Odyssey
The arts of ancient Egypt evolved through various dynasties, each contributing distinct styles and themes that shaped the visual landscape of the civilization. From the early dynastic period to the Ptolemaic era, the art of ancient Egypt underwent transformations influenced by political, social, and religious shifts.

Hieroglyphics, a system of writing that incorporated pictorial symbols, played a pivotal role in the artistic expression of ancient Egyptians. These hieroglyphs adorned monumental structures, including temples and tombs, providing both a written record and a visual language that conveyed the religious, political, and social narratives of the time.
2. Arts and Architecture: Temples, Tombs, and Monuments
The monumental architecture of ancient Egypt remains a testament to the grandeur and precision of the civilization. Temples, tombs, and other structures were not only utilitarian but also served as canvases for artistic expression.
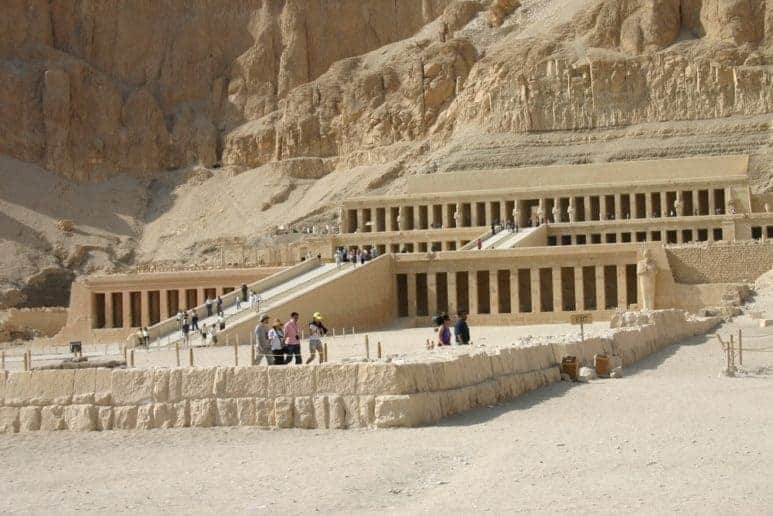

Temples, such as the iconic Temple of Karnak and the Temple of Luxor, were dedicated to deities and adorned with colossal statues, intricate reliefs, and hieroglyphic inscriptions. These temples served as both religious sanctuaries and symbolic representations of the pharaoh’s divine connection.

Tombs played a crucial role in ancient Egyptian art, particularly in the form of elaborate burial complexes like the Valley of the Kings. The walls of these tombs were adorned with intricate paintings and carvings depicting scenes from the deceased’s life, religious rituals, and journeys in the afterlife. Notable examples include the tomb of Tutankhamun, with its vivid depictions of the pharaoh’s journey to the underworld.
3. The Palette of Ancient Egyptian Art: Symbolism and Significance
The art of ancient Egypt was not merely decorative; it carried profound symbolic meaning and reflected the religious and cultural beliefs of the society. Symbolism played a crucial role in conveying messages about the afterlife, the divine order, and the earthly realm.
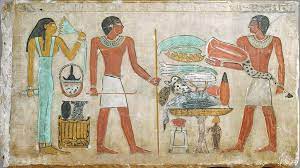
Colors held specific symbolic significance in ancient Egyptian art. For example, green represented fertility and rebirth, blue symbolized the heavens and the Nile, and gold symbolized the eternal and divine. The use of these colors in paintings and sculptures conveyed not only aesthetic beauty but also layers of meaning embedded in the culture’s cosmology.
Animal Symbolism was another prominent feature of ancient Egyptian art. Various animals held religious significance, such as the scarab beetle representing regeneration and protection, the lion symbolizing strength, and the ibis associated with wisdom and writing. These symbols adorned jewelry, statues, and amulets, emphasizing the interconnectedness of the natural world with the divine.
4. Portraits of Power: Statuary and Sculpture
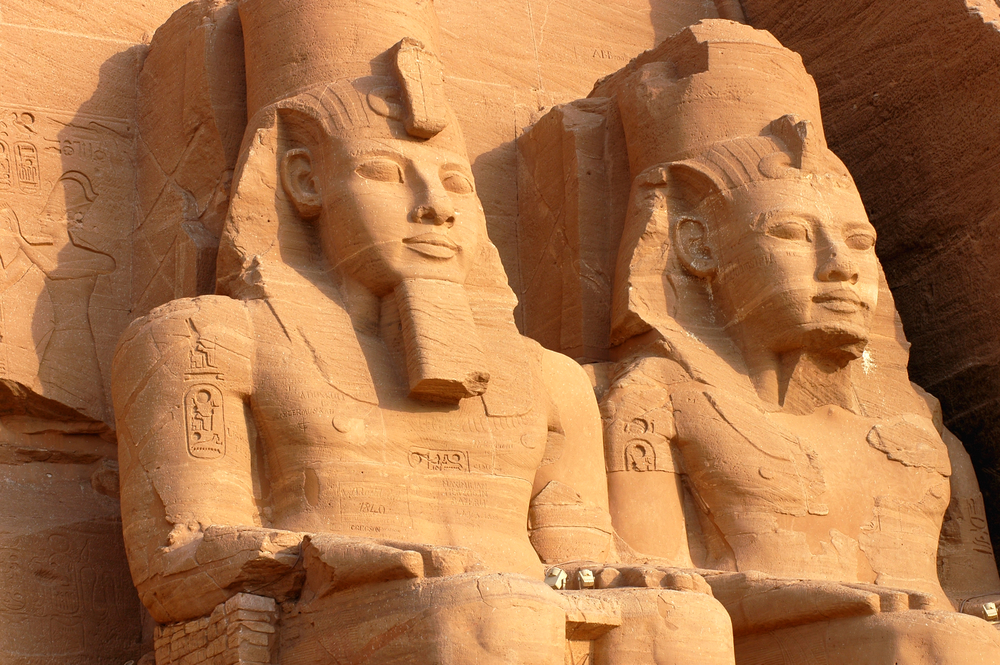
Sculpture played a central role in portraying the authority and divinity of the pharaohs. Colossal statues, such as the Great Sphinx of Giza and the statues of Ramses II, conveyed the majesty and power of the rulers. The rigidly formalized poses and idealized representations in these statues aimed to immortalize the pharaohs and emphasize their divine status.
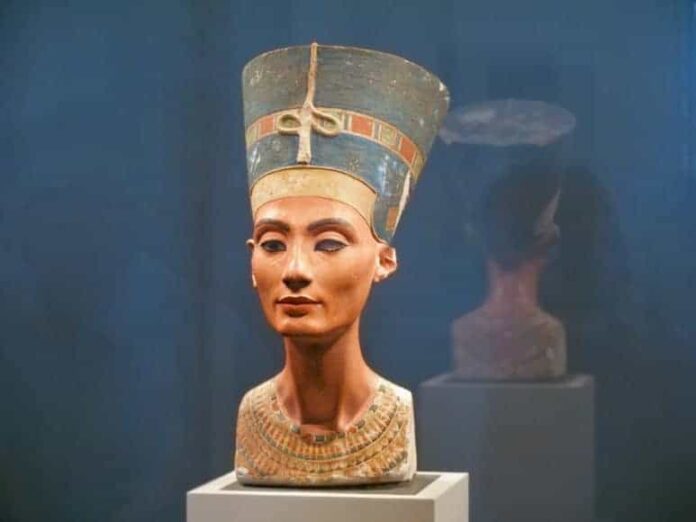
Busts and portraits of individuals, especially those from the elite class, depicted a more naturalistic representation. The sculptures captured intricate details of clothing, jewelry, and hairstyles, providing insights into the social hierarchy and fashion of the time. Notable examples include the famous bust of Nefertiti, renowned for its beauty and craftsmanship.
5. The Magic of Papyrus: Ancient Egyptian Paintings and Manuscripts
Papyrus, a plant native to the Nile Delta, served as a versatile medium for ancient Egyptian painters and scribes. Paintings on papyrus ranged from depictions of everyday life to religious ceremonies and mythological narratives. The vivid colors and detailed scenes reflected the Egyptians’ keen observation of their environment and their beliefs in the cyclical nature of life and death.
The Book of the Dead, a collection of religious texts and spells inscribed on papyrus, provided guidance for the deceased in the afterlife. These manuscripts were often illustrated with scenes depicting the soul’s journey through the underworld, encounters with deities, and the final judgment. The combination of text and images in the Book of the Dead exemplifies the holistic approach to art and spirituality in ancient Egypt.
6. Preservation and Rediscovery: Ancient Egyptian Art in the Modern Era
The preservation of ancient Egyptian art owes much to the dry climate of the region, which protected tombs and artifacts from decay. The meticulous efforts of archaeologists and conservators have allowed modern scholars to uncover and study the treasures of ancient Egypt.
The Rosetta Stone, discovered in 1799, played a pivotal role in deciphering ancient Egyptian hieroglyphics. This multilingual stone inscription, featuring text in Greek, Demotic script, and hieroglyphics, provided the key to understanding the once-undecipherable ancient writing system.

The discovery of Tutankhamun’s tomb by Howard Carter in 1922 revealed an unparalleled treasure trove of artifacts, offering insights into the material culture, artistry, and religious beliefs of ancient Egypt. The perfectly preserved burial chamber and its contents provided an invaluable window into the past.
A Legacy Written in Stone and Color
The arts of ancient Egypt, with their enduring beauty and profound symbolism, continue to captivate and inspire people around the world. From the colossal monuments that line the banks of the Nile to the delicate paintings on papyrus, ancient Egyptian art serves as a timeless testament to the creativity, spirituality, and cultural richness of this remarkable civilization.
As we explore the history of ancient Egyptian art, we uncover not only the stories of pharaohs and gods but also the daily lives, aspirations, and beliefs of a people who left an indelible mark on the tapestry of human history. The legacy of ancient Egyptian art is a treasure trove waiting to be discovered, inviting us to delve into a world where art and culture converged to create a civilization that defied the sands of time.

















![What Kind of Feedback Is Most Useful to an Artist? [Cartoon]](https://usaartnews.com/wp-content/uploads/khDBDPJT5M3BJCUUAxOzZZnOKIv66T3puxdhcXc0-80x60.jpg)







