Almost no other artist exercised such a decisive influence on European Baroque painting as Peter Paul Rubens (1577–1640) did. The Städel Museum in Frankfurt dedicates a comprehensive special exhibition to the world-renowned artist, which is on show from 8 February to 21 May 2018: Rubens. The Power of Transformation comprises about one hundred items— including thirty-one paintings and twenty-three drawings by the master—and explores a hitherto little-regarded aspect in his creative process.
The presentation reveals how profound the dialogue was into which Rubens entered with his predecessors’ and contemporaries’ achievements and fathoms the scope of their impact on the five decades of his production. Rubens’s extensive oeuvre reflects the influences of ancient sculpture as well as that of the later art from Italy and north of the Alps, from the masters towards the close of the fifteenth century to the artists of his own day.
Frequently, only a closer look will reveal how Rubens drew on the work of artists of different epochs: the exhibition offers an opportunity to comprehend the sometimes astonishing correlations in detail. The cross-genre presentation brings together paintings, drawings, prints, sculptures, and objets d’art. In addition to original sculptures dating from classical antiquity to the Renaissance, the show also encompasses paintings and prints by Rubens’s precursors and contemporaries, among them key works by Titian and Tintoretto, by Goltzius, Rottenhammer, and Elsheimer, as well as by Giambologna, Van Tetrode, and Van der Schardt.
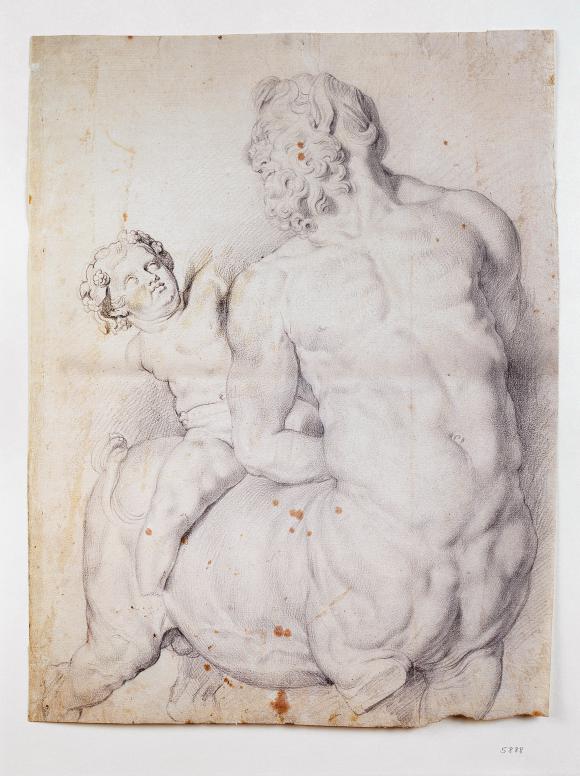

Centaur tamed by cupid, c. 1601/02
Black chalk on paper
Städel Director Philipp Demandt: “We are able to present an extraordinary artist’s genius in all its facets to our public with this large-scale exhibition project. The comprehensive show offers a fascinating view of Baroque masterpieces that have never ceased to spellbind the viewer.”
The ancient Roman sculpture of a crouching Venus preparing to take a bath provides another impressive example: Showing the same pose but conveying a completely different frame of mind, she has not merely been transmuted into a freezing Venus, the Venus Frigida (1614) but also into the goddess of Love lamenting her lover’s death (Venus mourning Adonis, c. 1614).
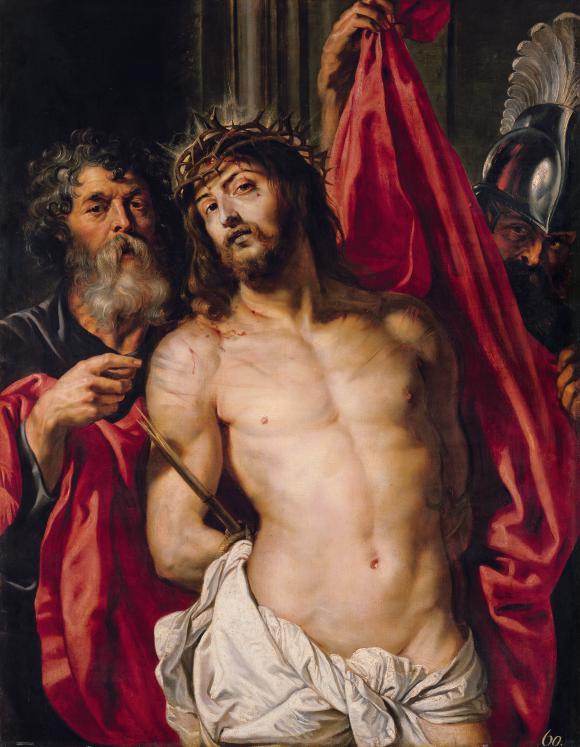

Crown of thorns (Ecce homo), c. 1612
A similarly arresting chain of motifs unravels from a work by the Flemish painter Michiel Coxcie depicting Cains’s murder of his brother (The Death of Abel, c. 1539). Rubens had acquired the study of the slain Abel by Coxcie in the form of a drawing, which he reworked in accordance with his understanding (Abel Slain by Cain, c. 1609). A short time after, the artist altered his solution to describe a tragically failing hero who has fallen backwards to the ground in an impressive drawing (Study of a falling man, c. 1610/11).
It was this study on which he directly modelled two further paintings on display in the exhibition: the brilliantly executed representation of the Death of Hippolytus (1611–1613) and his monumental Prometheus (1611/12–1618). Some years later, no lesser artist than Rembrandt (1606 – ca. 1669) would vie with Rubens’s masterpiece that excited wide admiration: His Blinding of Samson (1636), one of the Städel’s capital works, which can only be understood against the background of the artist’s study of Rubens, has, therefore, been included in the exhibition.
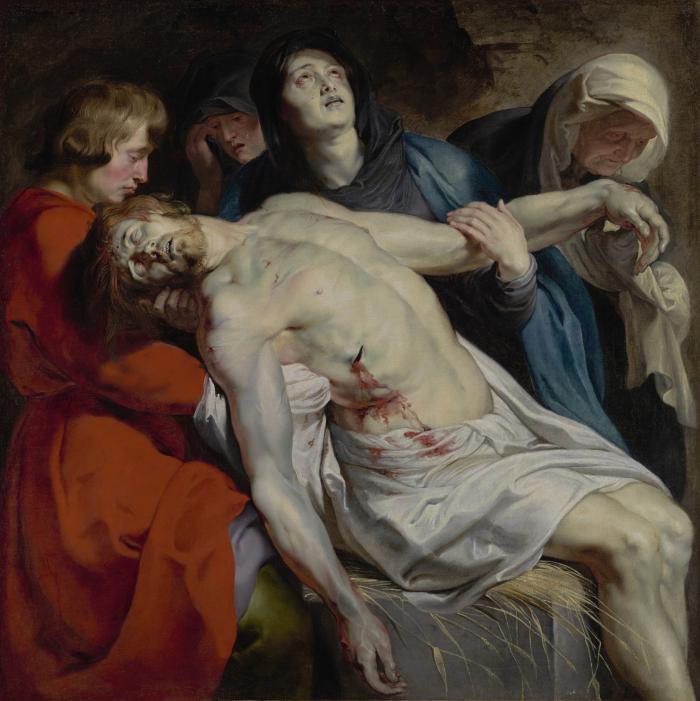
The Entombment, c. 1612
The direct comparison between works by Rubens and their models offers fascinating insights into the ingenious development of the master’s solutions and surprising motific metamorphoses, as well as his intense endeavours for an adequate format and the right form. The peculiarly modern, dynamic appearance of Rubens’s creations is frequently indebted to the very deliberate return to identifiable models, which the artist—in the understanding of the concept of ‘aemulatio’ crucial within his era’s theory of art—even tried to outdo. Each of the transformation processes resulted in a work that immediately enthralled the contemporary viewer and still fascinates us today. The special exhibition is a joint project of the Städel Museum and the Kunsthistorisches Museum in Vienna, five examples from whose rich holdings of works by Rubens have travelled to Frankfurt. Works by Rubens from the Städel’s collection have also been incorporated into the presentation, among them the oil sketch The Mystic Marriage of St Catherine (1628, draft for the high altarpiece of the Church of St Augustine in Antwerp) as well as several important items from its Department of Prints and Drawings.
Peter Paul Rubens was born the sixth of seven children in the city of Siegen, Westphalia, in 1577 and died in Antwerp on May 30, 1640. When still a young man, Rubens won international renown as an extraordinarily innovative artist. Yet Rubens was not only a painter but also an art theorist and collector, a respected discussion partner of European scholars and princes, and a diplomat in European employ—all this with Antwerp, the centre of his life, as a starting point.
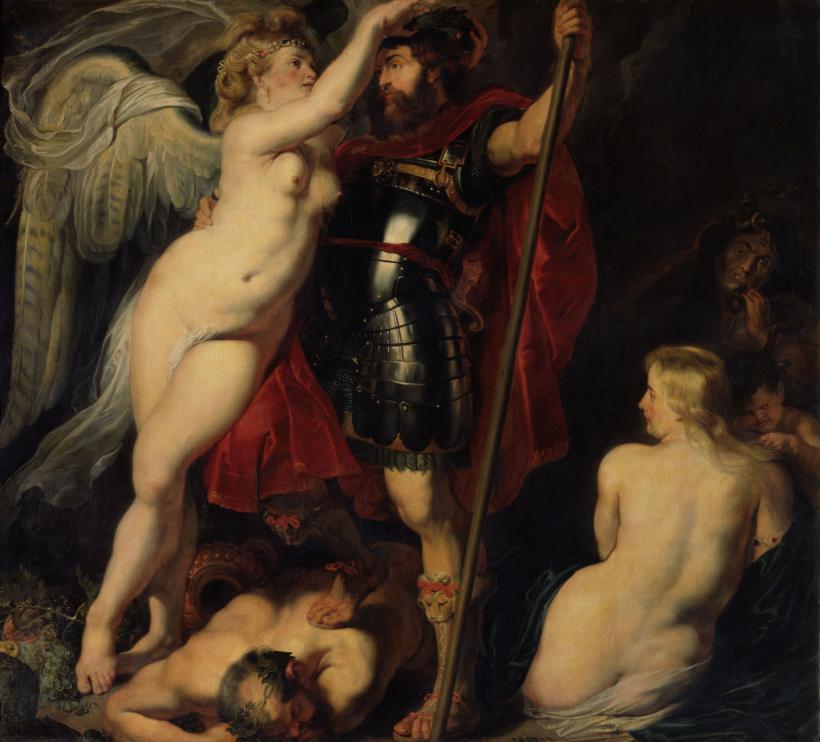

The hero of virtue, crowned by victory, c. 1615/16
With more than fifty works in churches and museums and the Rubenshuis with its living quarters and adjacent studio, the artist and his work are still present in his hometown in an exceptional manner today. Rubens studied under three teachers, among them the Antwerp painter Otto van Veen (1556–1629). At the age of only twenty-one, he entered the Guild of St Luke, the city’s guild of painters, as a master in 1598, getting to know Antwerp’s intellectual circles.
In 1600, he travelled to Italy, where he stayed for eight years. This time—and especially the ancient sculptures he became familiar with then—had a lasting effect on his work. After his return to Antwerp in 1608, Rubens was appointed court painter to Albert, Archduke of Austria, and his wife Isabella Clara Eugenia, Catholic sovereigns of the Southern Netherlands, and married Isabella Brant, the city clerk’s daughter. Rubens had become one of Europe’s most soughtafter painters, who created paintings for kings and princes, political leaders and diplomats. He decided to buy a house in 1610 for his workshop and his family, which he had converted into a small Italian-style city palace.
After his first wife had passed away in 1626 and the Archduke of Austria’s death, Rubens became Isabella’s adviser, travelling through Europe in diplomatic mission from 1625 to 1628 to negotiate a possible peace between Spain and England and to campaign for ending the conflicts between the United Provinces in the north and the Southern Netherlands. It was not least thanks to his skill at negotiating that the Treaty of Madrid between England and Spain could be signed in 1630.

























